Meals ecosysm – Meals ecosystems, the intricate tapestry of life and sustenance, kind the cornerstone of our planet’s ecological stability. They’re dynamic and interconnected networks that embody all residing organisms, from the tiniest microorganisms to the majestic whales, and the non-living elements of their setting.
Inside these ecosystems, an enchanting dance of interactions unfolds, the place every species performs a vital function in sustaining the fragile equilibrium. Producers, customers, decomposers, and abiotic elements intertwine, creating a posh internet of power movement and nutrient biking that sustains life on Earth.
Meals Ecosystem Parts
A meals ecosystem is a group of residing organisms at the side of the nonliving elements of their setting (issues like air, water and soil), interacting as a system. The meals ecosystem could be small or massive. Ecosystems are the key elements of the biosphere, the a part of Earth that’s inhabited by residing issues.
Meals ecosystems are labeled into two predominant varieties: pure ecosystems and synthetic ecosystems. Pure ecosystems are shaped naturally with out human intervention, whereas synthetic ecosystems are created and maintained by people, akin to farms and gardens.
Producers
Producers are organisms that may make their very own meals from inorganic matter. They’re the inspiration of the meals ecosystem, offering power for all different organisms. Crops are the first producers in most ecosystems, utilizing daylight, water, and carbon dioxide to provide glucose via photosynthesis.
- Examples:Crops, algae, and a few micro organism
- Position:Convert daylight into power (glucose) via photosynthesis
Shoppers
Shoppers are organisms that can’t make their very own meals and should devour different organisms to acquire power. Shoppers are labeled into totally different trophic ranges primarily based on their feeding habits.
- Main customers (herbivores):Feed straight on producers
- Secondary customers (carnivores):Feed on major customers
- Tertiary customers (prime predators):Feed on secondary customers
Decomposers, Meals ecosysm
Decomposers are organisms that break down lifeless organisms and waste merchandise into easier substances. They play a vital function in recycling vitamins again into the ecosystem.
- Examples:Micro organism, fungi, and worms
- Position:Break down natural matter into inorganic vitamins
Abiotic Components
Abiotic elements are nonliving elements of the ecosystem that affect the survival and distribution of organisms. These elements embrace:
- Local weather:Temperature, precipitation, and daylight
- Water:Availability and high quality
- Soil:Kind, fertility, and pH
- Topography:Elevation, slope, and facet
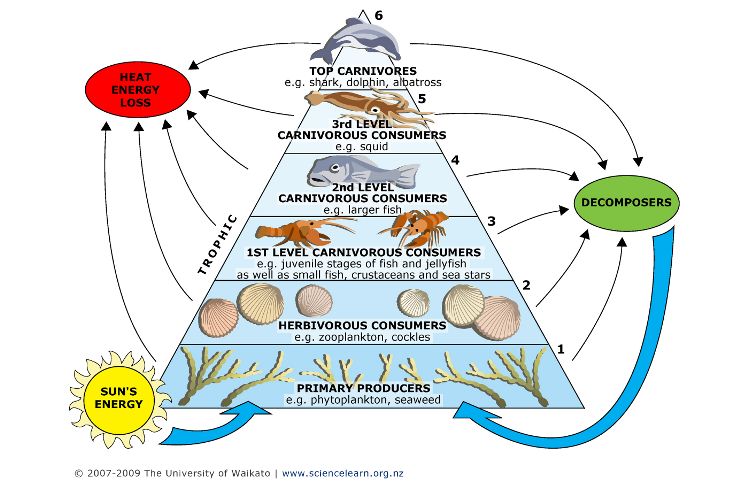
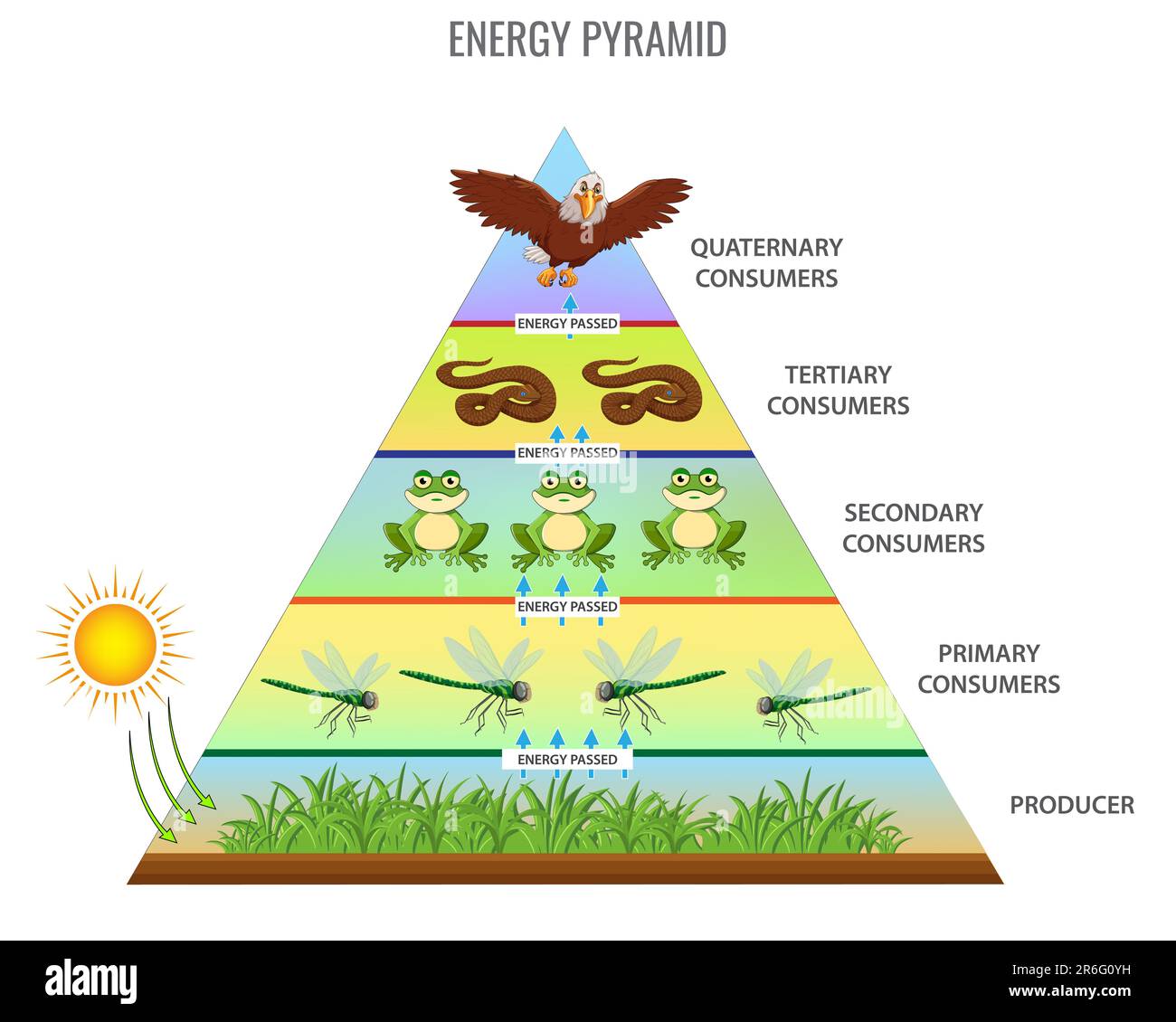
Meals Webs and Trophic Ranges
Meals webs depict the intricate connections between organisms in an ecosystem primarily based on their feeding relationships. They prolong past easy meals chains, displaying the interdependence of a number of species and the movement of power via totally different trophic ranges.
Trophic ranges classify organisms primarily based on their place within the meals internet. Every degree represents a step within the switch of power from producers to prime predators.
Trophic Ranges
- Producers:Autotrophic organisms (e.g., crops) that convert daylight into power via photosynthesis.
- Main Shoppers:Herbivores (e.g., deer) that feed straight on producers.
- Secondary Shoppers:Carnivores (e.g., foxes) that feed on major customers.
- Tertiary Shoppers:Carnivores (e.g., wolves) that feed on secondary customers.
- Prime Predators:Organisms (e.g., lions) on the highest trophic degree, with no predators.
Simplified Meals Net
Contemplate a simplified meals internet in a forest ecosystem:
Producers:Bushes, shrubs, and grasses
Main Shoppers:Deer, rabbits, and mice
Secondary Shoppers:Foxes, owls, and snakes
Tertiary Shoppers:Wolves and mountain lions
Prime Predators:None
Vitality flows from producers to prime predators, with every trophic degree shedding roughly 90% of the power it consumes.
Vitality Stream and Nutrient Biking: Meals Ecosysm
Vitality movement and nutrient biking are elementary processes inside meals ecosystems, making certain the continual availability of power and vitamins for organisms at totally different trophic ranges. Vitality enters the ecosystem via major producers, akin to crops, and flows unidirectionally via customers, whereas vitamins are recycled and reused inside the system.
Vitality Stream
- Vitality enters the ecosystem via daylight, which is captured by crops throughout photosynthesis.
- Crops use this power to provide natural matter, which is consumed by herbivores (major customers).
- Herbivores are consumed by carnivores (secondary customers), and so forth.
- At every trophic degree, a good portion of power is misplaced as warmth as a consequence of metabolic processes.
- Solely about 10% of power is transferred from one trophic degree to the following, leading to a pyramid-shaped power movement diagram.
Nutrient Biking
- Vitamins, akin to nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium, are important for plant development and are recycled inside the ecosystem.
- Decomposers, akin to micro organism and fungi, break down lifeless organisms and launch vitamins again into the soil.
- Crops soak up these vitamins and use them for development, whereas animals get hold of vitamins by consuming crops or different animals.
- Nutrient biking ensures a steady provide of important parts for organisms in any respect trophic ranges.
The processes of power movement and nutrient biking are interconnected and important for the steadiness and functioning of meals ecosystems. They guarantee a steady movement of power and vitamins, supporting the survival and development of organisms at totally different trophic ranges.
Ecosystem Companies and Human Impression

Meals ecosystems present a variety of companies which might be important for human well-being. These companies embrace:
- Meals manufacturing: Meals ecosystems present the overwhelming majority of the meals we eat. Crops convert daylight into power via photosynthesis, which is then handed up the meals chain to animals. People are on the prime of many meals chains, and we depend on crops and animals for our meals.
- Water purification: Meals ecosystems assist to purify water by filtering out pollution and sediment. Crops and animals in meals ecosystems additionally assist to control water movement, which might forestall flooding and erosion.
- Carbon sequestration: Meals ecosystems assist to take away carbon dioxide from the environment. Crops soak up carbon dioxide throughout photosynthesis, and animals launch carbon dioxide once they breathe. Nevertheless, the web impact of meals ecosystems is to take away carbon dioxide from the environment, which helps to mitigate local weather change.
Human Impression on Meals Ecosystems
Human actions can have a major affect on meals ecosystems. These impacts embrace:
- Air pollution: Air pollution can hurt crops and animals in meals ecosystems. For instance, air air pollution can harm crops, and water air pollution can hurt fish and different aquatic organisms.
- Habitat loss: Habitat loss happens when pure areas are transformed to different makes use of, akin to agriculture or growth. Habitat loss can scale back the quantity of meals and shelter out there to crops and animals, and it might additionally disrupt meals chains.
- Local weather change: Local weather change is inflicting modifications in temperature, precipitation, and different environmental circumstances. These modifications can have a major affect on meals ecosystems. For instance, rising temperatures could cause crops and animals to maneuver to new areas, and modifications in precipitation can have an effect on the supply of water for crops and animals.
Meals Safety and Sustainability
Meals safety is a crucial facet of human well-being, making certain entry to adequate, secure, and nutritious meals for all people always. It’s intently intertwined with the steadiness and productiveness of meals ecosystems, which offer the inspiration for meals manufacturing and distribution.
Sustaining sustainable meals ecosystems is paramount within the face of rising inhabitants and environmental pressures. Because the human inhabitants continues to broaden, so does the demand for meals, placing a pressure on pure sources and ecosystems. Local weather change, air pollution, and land degradation additional exacerbate these challenges, disrupting meals manufacturing and distribution methods.
Challenges to Meals Safety and Sustainability
- Rising inhabitants and urbanization
- Local weather change and excessive climate occasions
- Air pollution and degradation of pure sources
- Unsustainable agricultural practices
- Inequitable distribution of meals
Alternatives for Meals Safety and Sustainability
- Investing in sustainable agriculture practices
- Decreasing meals waste and loss
- Selling dietary variety and native meals methods
- Enhancing meals distribution and entry
- Educating customers about sustainable meals decisions
By addressing these challenges and embracing these alternatives, we are able to improve the resilience of meals ecosystems and guarantee meals safety for current and future generations.
Case Research and Actual-World Examples
Meals ecosystems exhibit numerous traits and challenges worldwide. Case research and real-world examples present beneficial insights into their complexities and administration methods.
The Serengeti Ecosystem
The Serengeti ecosystem in East Africa is famend for its huge grasslands, numerous wildlife, and sophisticated meals webs. The annual wildebeest migration, involving hundreds of thousands of animals, is a spectacle that highlights the interdependence of species and the ecosystem’s resilience. Nevertheless, the ecosystem faces challenges akin to habitat loss, poaching, and local weather change, necessitating cautious administration to protect its ecological integrity.
The Chesapeake Bay Ecosystem
The Chesapeake Bay ecosystem in the USA is a big estuary with a wealthy historical past of fisheries and seafood manufacturing. Nevertheless, overfishing, nutrient air pollution, and habitat degradation have led to a decline in its ecological well being. Administration methods, together with fishing rules, nutrient discount plans, and habitat restoration efforts, are being applied to revive the ecosystem’s productiveness and biodiversity.
The Effectiveness of Administration Methods
The effectiveness of administration methods for preserving and enhancing meals ecosystems is dependent upon numerous elements, together with the precise ecosystem, the administration objectives, and the extent of stakeholder involvement. Case research have proven that collaborative approaches, adaptive administration strategies, and science-based decision-making can contribute to the profitable implementation and outcomes of administration methods.
FAQ
What’s a meals ecosystem?
A meals ecosystem is a group of residing organisms at the side of the nonliving elements of their setting (issues like air, water and soil), interacting as a system. These biotic and abiotic elements are linked collectively via nutrient cycles and power flows.
What are the totally different elements of a meals ecosystem?
Meals ecosystems include producers, customers, decomposers, and abiotic elements. Producers are organisms that may make their very own meals from inorganic matter, customers are organisms that can’t make their very own meals and should eat different organisms, decomposers are organisms that break down lifeless organisms, and abiotic elements are nonliving issues that have an effect on the ecosystem, akin to daylight, water, and temperature.
What’s the significance of meals ecosystems?
Meals ecosystems are important for all times on Earth. They supply us with meals, clear water, and air, and so they assist to control the local weather. Meals ecosystems additionally present us with many different advantages, akin to recreation, tourism, and schooling.



