Within the coronary heart of arid areas lies a charming ecosystem the place life adapts and thrives in extraordinary methods. Delving into the meals chain for desert, we uncover a captivating net of interdependence and resilience that sustains this distinctive atmosphere.
From the smallest bugs to the majestic predators, every organism performs an important position in sustaining the fragile steadiness of the desert ecosystem.
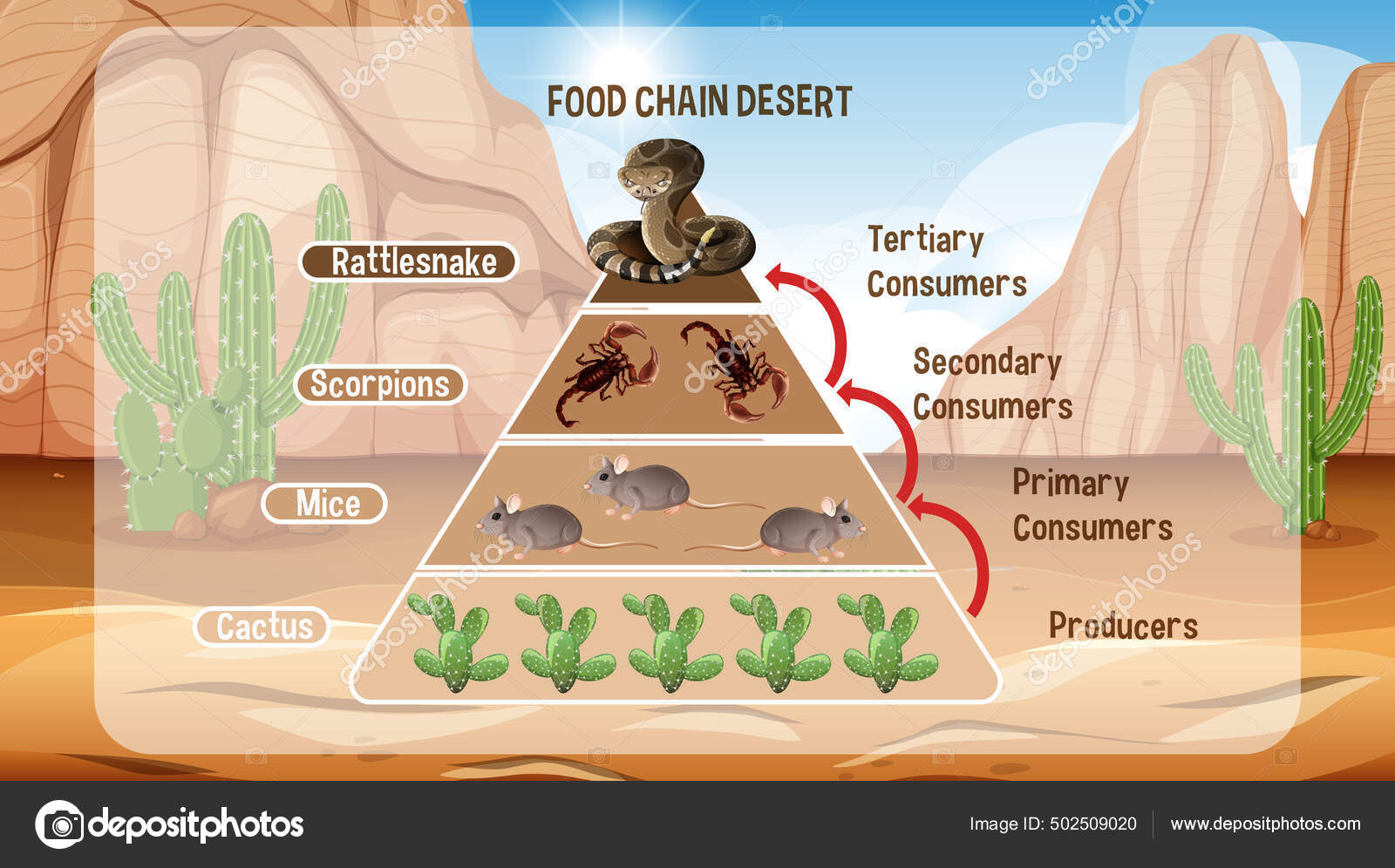
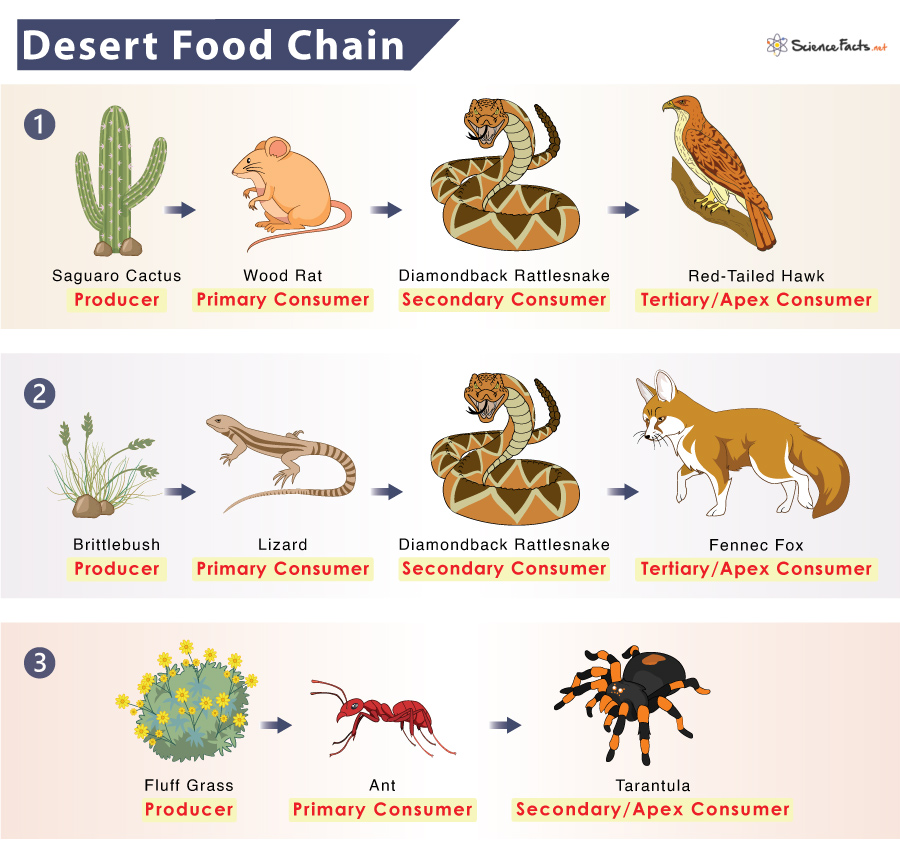
Desert Meals Chain Construction
The desert meals chain, not like different ecosystems, displays a singular construction because of the shortage of water and restricted vegetation. It contains numerous trophic ranges, every enjoying an important position in sustaining the fragile steadiness of the desert ecosystem.
Producers
The muse of the desert meals chain lies with the producers, primarily vegetation and sure microorganisms. These organisms harness daylight by way of photosynthesis, changing it into energy-rich compounds that function the first supply of sustenance for all different organisms within the desert ecosystem.
Main Customers
Main customers are herbivores that feed immediately on the producers. These embrace bugs, rodents, and reptiles. By consuming vegetation, they acquire the mandatory vitamins to maintain themselves and supply an important hyperlink between producers and better trophic ranges.
Secondary Customers
Secondary customers are carnivores that prey on main customers. Examples embrace snakes, birds, and small mammals. They play an important position in regulating the populations of herbivores, stopping overgrazing and sustaining the steadiness of the desert ecosystem.
Tertiary Customers
Tertiary customers are apex predators that occupy the very best trophic degree. These embrace giant carnivores comparable to coyotes, wolves, and eagles. They play a essential position in controlling the populations of secondary customers and making certain the steadiness of the desert ecosystem.
Decomposers
Decomposers, comparable to micro organism and fungi, are important for nutrient biking within the desert ecosystem. They break down useless organisms and natural matter, releasing important vitamins again into the soil, which may then be utilized by producers.
Diversifications for Survival

Within the harsh desert atmosphere, vegetation and animals have developed exceptional diversifications to outlive the intense circumstances. These diversifications allow them to acquire meals and water in a panorama the place assets are scarce.
Plant Diversifications, Meals chain for desert
- Succulence:Desert vegetation retailer water of their fleshy stems and leaves, permitting them to resist lengthy durations of drought.
- Deep Root Programs:Vegetation develop intensive root methods that attain deep into the bottom, accessing water sources unavailable to shallow-rooted species.
- Thick Cuticles:Leaves and stems are lined with a thick cuticle that reduces water loss by way of evaporation.
- CAM Photosynthesis:Some desert vegetation use CAM (Crassulacean Acid Metabolism) photosynthesis, which minimizes water loss by opening their stomata at evening to soak up carbon dioxide.
Animal Diversifications
- Nocturnal Exercise:Many desert animals are nocturnal, avoiding the extraordinary warmth and water loss through the day.
- Water Conservation:Animals have environment friendly kidneys and produce concentrated urine to attenuate water loss.
- Behavioral Diversifications:Animals search shelter underneath rocks or in burrows to flee the solar and preserve water.
- Environment friendly Foraging:Desert animals have specialised diets and feeding methods to maximise meals consumption whereas minimizing power expenditure.
Vitality Move and Nutrient Biking
The desert meals chain, like all ecosystems, depends on the switch of power and biking of vitamins to maintain its delicate steadiness. Understanding this movement and biking is essential for comprehending the desert’s ecological dynamics.
Vitality, initially captured by producers by way of photosynthesis, flows by way of the meals chain as organisms devour one another. Main customers, comparable to herbivores, acquire power by feeding on producers. Secondary customers, like carnivores, devour main customers, and so forth. With every switch, power is misplaced as warmth, leading to a gradual lower in power availability at larger trophic ranges.
Nutrient Biking
Nutrient biking entails the transformation and motion of important components inside the ecosystem. Producers take up vitamins from the soil and environment, that are then handed up the meals chain by way of consumption. Decomposers, comparable to micro organism and fungi, break down useless organisms and natural matter, releasing vitamins again into the soil.
This course of ensures a steady provide of vitamins for plant development and first manufacturing.
Components Affecting Vitality and Nutrient Availability
- Local weather:Temperature and precipitation patterns affect plant development and nutrient availability. Excessive warmth and drought can scale back plant productiveness, impacting power movement and nutrient biking.
- Soil Situations:Soil high quality impacts nutrient availability for vegetation. Nutrient-poor soils restrict plant development, lowering power movement and nutrient biking.
- Human Actions:Land use adjustments, grazing, and air pollution can disrupt nutrient biking and power movement, affecting the steadiness of desert ecosystems.
Interdependence and Symbiosis
The desert meals chain is a posh net of interactions between organisms, the place interdependence and symbiosis play essential roles in sustaining the steadiness and resilience of the ecosystem.
Symbiotic relationships within the desert meals chain might be categorized into three major varieties: mutualism, commensalism, and parasitism.
Mutualism
- Desert vegetation and pollinators:Desert vegetation depend on pollinators, comparable to bugs and birds, to switch pollen between flowers, enabling replica. In return, pollinators profit from the nectar and pollen supplied by the vegetation as a meals supply.
- Ants and acacia timber:Ants construct nests within the hole thorns of acacia timber, defending them from herbivores. The ants additionally feed on the nectar produced by the timber, whereas the timber profit from the ants’ safety.
Commensalism
- Mistletoe and desert timber:Mistletoe vegetation develop on the branches of desert timber, utilizing them as assist. The mistletoe doesn’t hurt the timber, nevertheless it advantages from the daylight and vitamins accessible within the tree’s cover.
- Rodents and burrow-dwelling animals:Rodents dig burrows within the desert, which give shelter for different animals, comparable to lizards and snakes. The rodents don’t profit from the presence of those animals, however the latter profit from the shelter supplied by the burrows.
Parasitism
- Fleas and desert animals:Fleas are exterior parasites that feed on the blood of desert animals. The animals endure from the lack of blood and might change into weakened or diseased, whereas the fleas profit from the vitamins obtained from their hosts.
- Tapeworms and desert predators:Tapeworms are inner parasites that stay within the digestive tracts of desert predators. They take up vitamins from the predators’ meals, inflicting malnutrition and well being issues within the host animals.
Disturbances and Resilience
Desert meals chains, like all ecosystems, face numerous disturbances that may alter their construction and dynamics. Understanding these disturbances and the resilience mechanisms that allow the desert meals chain to recuperate is essential for its conservation and administration.
Forms of Disturbances
- Local weather variability and extremes:Deserts expertise excessive temperature fluctuations, droughts, and floods, which may impression plant and animal survival.
- Human actions:Land use adjustments, habitat fragmentation, and air pollution can disrupt meals chains by altering habitat availability and useful resource abundance.
- Invasive species:Non-native species can compete with native species for assets, resulting in inhabitants declines and ecosystem disruption.
- Hearth:Wildfires can burn vegetation, destroying habitat and meals sources for animals.
- Illness outbreaks:Pathogens can unfold quickly by way of desert populations, inflicting important mortality and disrupting meals chains.
Impression on Ecosystem Construction and Dynamics
Disturbances can impression desert meals chains in a number of methods:
- Altered species composition:Disturbances can favor sure species over others, resulting in adjustments in neighborhood construction.
- Decreased biodiversity:Excessive disturbances can lead to species extinctions and a decline in total biodiversity.
- Disrupted power movement:Disturbances can disrupt power switch between trophic ranges, affecting the supply of meals assets.
- Altered nutrient biking:Disturbances can have an effect on nutrient availability and biking processes, impacting plant development and animal well being.
Resilience Mechanisms
Regardless of these disturbances, desert meals chains exhibit resilience, enabling them to recuperate and keep ecosystem perform. Key resilience mechanisms embrace:
- Diversifications to excessive circumstances:Desert species have developed physiological and behavioral diversifications that enable them to outlive in harsh circumstances.
- Seed banks and dormancy:Many desert vegetation produce dormant seeds that may stay viable for prolonged durations, permitting them to recolonize after disturbances.
- Dispersal and colonization:Desert animals and vegetation have tailored to disperse lengthy distances, facilitating recolonization of disturbed areas.
- Mutualistic relationships:Symbiotic relationships between species, comparable to pollination and seed dispersal, improve ecosystem stability and resilience.
- Ecological reminiscence:Desert ecosystems have a “reminiscence” of previous disturbances, which influences their response to future occasions.
Human Impacts: Meals Chain For Desert
Human actions have a major impression on desert meals chains. These impacts might be direct, comparable to habitat loss and air pollution, or oblique, comparable to local weather change.
Habitat lossis among the most vital threats to abandon meals chains. As human populations develop, so does the demand for land for growth. This growth can result in the destruction of desert habitats, which may in flip result in the lack of meals sources for desert animals.
Air pollution
Air pollution is one other main menace to abandon meals chains. Pollution can enter the desert atmosphere by way of a wide range of sources, together with industrial actions, agricultural runoff, and automobile emissions. These pollution can hurt desert animals immediately, or they will not directly hurt them by contaminating their meals sources.
Local weather Change
Local weather change can also be a significant menace to abandon meals chains. Because the local weather adjustments, the distribution of desert vegetation and animals is prone to change. This might result in the lack of meals sources for some desert animals, and it might additionally make it tougher for them to search out mates.
Mitigating these impactsis important for conserving desert ecosystems. There are a variety of issues that may be accomplished to mitigate the impacts of human actions on desert meals chains, together with:
- Defending and restoring desert habitats
- Lowering air pollution
- Addressing local weather change
Useful Solutions
What are the important thing diversifications that allow organisms to outlive in desert circumstances?
Organisms within the desert have developed exceptional diversifications, comparable to water storage mechanisms, specialised feeding habits, and physiological diversifications to preserve water and power.
How does the movement of power by way of the desert meals chain impression nutrient availability?
The movement of power by way of the meals chain determines the supply of vitamins, as producers convert daylight into power and customers make the most of these vitamins for development and replica.




